The goal is to generate an extensive Antibody Library of phage-displayed human scFV with a 6.7 * 109 member count that could serve the application in the respective industries and research laboratories. The Antibody Library is to be generated with improvising steps in library construction. Fourteen different protein antigens were under the affinity to select antibodies from the library. The goal is the generation of reagents from these large libraries that study the function of gene products identified by the genome projects.
Methods
- Construction of the VH-VL Library.
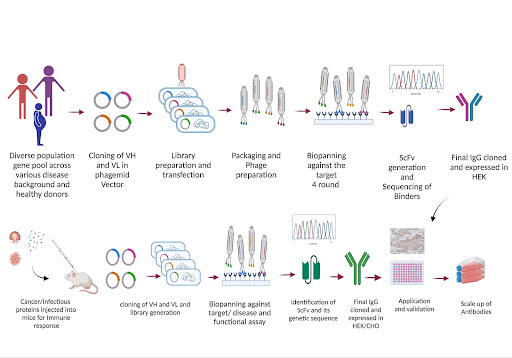
Total RNA is prepared when different samples are taken from human spleen cells and human peripheral blood lymphocytes. The cDNA synthesised using the total RNA is primed with Human lgG Forward and Reverse primer. This VH-VL gene repertoire is amplified from cDNA of Lymphocyte and cloned in Phagemid vector.
The resulting antibody gene library is transformed in E.coli TG1 cells and Phages are prepared to display the gene of VH-VL on Phages PIII gene which is tail of phages.
- Selection of Phage Antibodies.
Phagemid particles in the antibody library are rescued and scaled up. The specific phage-display scFV were selected with proteins that were affinity selected and are absorbed in Immunotubes.
Immunotubes are coated overnight and purified from suspension culture. The phage eluted from each selection is put for transfecting E.coli TG1 cells. The rescue plating is done 3 to 4 times each to analyse specific antigen binding by ELISA technique till we achieve high binding clones.
- Antibody Binding Specificity.
The antibody binding specificity is determined from all scFV by the ELISA technique, which is proceeded with using a target antigen that has nine different proteins than the desired ones as substrates in the process. The Antigen is subsequently reduced in concentration in order to achieve a very high affinity and specificity antibody.
- scFv Purification and Affinity Measurements.
For purification, scFV genes are taken and subcloned, expressed, and purified to homogeneity. scFV dissociation equilibrium constants (Kd) is calculated from association constant (Ko) and dissociation (Koff) rate constants; these are determined with the surface plasmon resonance in a BIAcore.
Results
- Library Construction.
The large antibody library was created when the routine isolation was done of high-affinity scFV antibodies on the target protein. The generated library plays a role in optimising every step that comes with library construction that promotes the efficiency of the scFV gene assembly and improvises the cloning.
These library generated products are of 12 ligation reactions that are associated with 36 electroporations. With the diverse repertoires created, there is V gene repertoires pool construction.
- Selection and Characterization of Antigen-Specific scFv.
With the ELISA technique, the binding specificity of the antigen is used to recognise the different scFvs in and around the antigens. The small number of clones was the one selected after analysis, and the screening would yield more amount of additional antibodies. The binding of scFV with the antigens are the most specific one. These antibodies are further developed into different format and a recombinant clone is developed to produce IgG. These IgG developed are assessed on parameters for development of lead antibody drug molecule.
Discussion
The scFv large antibody library generated is efficient in producing the antibodies that could be used extensively. The difference in criteria and the validated results come with the above method for constructing the extensive antibody library. The rapid production of antibody libraries is set to affinity selection and recognises antigens at a higher percentage.
In addition, these antibodies and isolated scFVs serve as functional reagents with the different assays such as ELISA, immunofluorescence, Western Blotting, Epitope Mapping, and more.
At GeNext Genomics, we take pride in building Antibody Library that helps serve the industry with high-quality products and services. Our clients put a demand, and our skilled research scientists and experienced professionals know their way to build the required product.
We serve with utmost precision and develop an accurate Antibody Library that helps you reach your research goals and achieve milestones. We help the clients by serving them with industry standardised production that gives high-quality results.
Comments
Post a Comment